Leetcode Day 42 - Monotone stack Advanced
42 Trapping Rain Water | 84 Largest Rectangle in Histogram
Monotone stack
| Diff | Problem | Python | Java |
|---|---|---|---|
 | 42 Trapping Rain Water | ✅ | |
 | 84 Largest Rectangle in Histogram | ✅ |
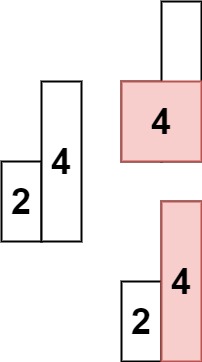
Trapping Rain Water
Given n non-negative integers representing an elevation map where the width of each bar is 1, compute how much water it can trap after raining.
Example 1
1
2
3
Input: height = [0,1,0,2,1,0,1,3,2,1,2,1]
Output: 6
Explanation: The above elevation map (black section) is represented by array [0,1,0,2,1,0,1,3,2,1,2,1]. In this case, 6 units of rain water (blue section) are being trapped.
Example 2
1
2
Input: height = [4,2,0,3,2,5]
Output: 9
Solution
Double Pointers
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
class Solution(object):
def trap(self, height):
h = len(height)
max_left = [0] * h
max_left[0] = height[0]
max_right = [0] * h
max_right[-1] = height[-1]
for i in range(1,h):
max_left[i] = max(height[i], max_left[i - 1])
for j in range(h - 2, -1, -1):
max_right[j] = max(height[j], max_right[j + 1])
water = 0
for num in range(1, h - 1):
water += max(min(max_left[num - 1], max_right[num + 1]) - height[num], 0)
return water
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
class Solution(object):
def trap(self, height):
left = 0
right = len(height) - 1
left_max = height[0]
right_max = height[len(height) - 1]
water = 0
while left < right:
if left_max < right_max:
left += 1
if left_max < height[left]:
left_max = height[left]
else:
water += left_max - height[left]
else:
right -= 1
if right_max < height[right]:
right_max = height[right]
else:
water += right_max - height[right]
return water
Monotone stack
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
class Solution(object):
def trap(self, height):
stack = [0]
water = 0
for i in range(1, len(height)):
if height[i] < height[stack[-1]]:
stack.append(i)
elif height[i] == height[stack[-1]]:
stack[-1] = i
else:
while len(stack) > 0 and height[i] > height[stack[-1]]:
if len(stack) > 1:
water += (i - stack[-2] - 1) * (min(height[i], height[stack[-2]]) - height[stack[-1]])
stack.pop()
stack.append(i)
return water
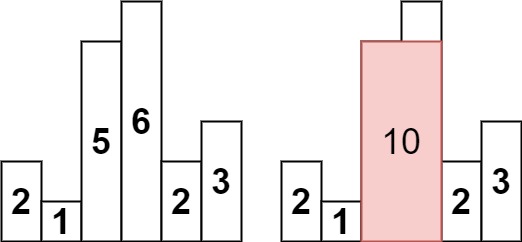
Largest Rectangle in Histogram
Given an array of integers heights representing the histogram’s bar height where the width of each bar is 1, return the area of the largest rectangle in the histogram.
Example 1
1
2
3
4
Input: heights = [2,1,5,6,2,3]
Output: 10
Explanation: The above is a histogram where width of each bar is 1.
The largest rectangle is shown in the red area, which has an area = 10 units.
Example 2
1
2
Input: heights = [2,4]
Output: 4
Solution
Python
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
class Solution:
def largestRectangleArea(self, heights):
if not heights:
return 0
max_area = 0
stack = []
n = len(heights)
for i in range(n + 1):
while stack and (i == n or heights[i] < heights[stack[-1]]):
h = heights[stack.pop()]
w = i if not stack else i - stack[-1] - 1
max_area = max(max_area, h * w)
stack.append(i)
return max_area
Reference
Leetcode-42 Trapping Rain Water: https://leetcode.com/problems/trapping-rain-water/description/. ↩︎
代码随想录-接雨水: https://programmercarl.com/0042.接雨水.html. ↩︎
Leetcode-84 Largest Rectangle in Histogram: https://leetcode.com/problems/largest-rectangle-in-histogram/description/. ↩︎
代码随想录-柱状图中最大的矩形: https://programmercarl.com/0084.柱状图中最大的矩形.html. ↩︎
This post is licensed under CC BY 4.0 by the author.