Leetcode Day 17 - Binary Search Tree: Insertion, Deletion, and LCA
Focuses on essential binary search tree (BST) operations, including finding the lowest common ancestor, inserting new nodes, and deleting nodes from a BST while maintaining its properties.
Binary Tree
| Diff | Problem | Python | Java |
|---|---|---|---|
 | 235 Lowest Common Ancestor of a Binary Search Tree | ✅ | |
 | 701 Insert into a Binary Search Tree | ✅ | |
 | 450 Delete Node in a BST | ✅ |
Lowest Common Ancestor of a Binary Search Tree
Given a binary search tree (BST), find the lowest common ancestor (LCA) node of two given nodes in the BST.
According to the definition of LCA on Wikipedia: “The lowest common ancestor is defined between two nodes p and q as the lowest node in T that has both p and q as descendants (where we allow a node to be a descendant of itself).”
Example 1
1
2
3
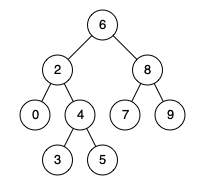
Input: root = [6,2,8,0,4,7,9,null,null,3,5], p = 2, q = 8
Output: 6
Explanation: The LCA of nodes 2 and 8 is 6.
Example 2
1
2
3
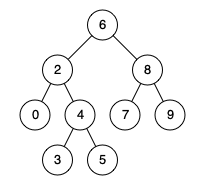
Input: root = [6,2,8,0,4,7,9,null,null,3,5], p = 2, q = 4
Output: 2
Explanation: The LCA of nodes 2 and 4 is 2, since a node can be a descendant of itself according to the LCA definition.
Example 3
1
2
Input: root = [2,1], p = 2, q = 1
Output: 2
Solution
Python
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
class Solution(object):
def lowestCommonAncestor(self, root, p, q):
if root is None:
return None
if (p.val <= root.val and q.val >= root.val) or (p.val >= root.val and q.val <= root.val):
return root
if p.val <= root.val and q.val <= root.val:
return self.lowestCommonAncestor(root.left, p, q)
if p.val >= root.val and q.val >= root.val:
return self.lowestCommonAncestor(root.right, p, q)
Insert into a Binary Search Tree
You are given the root node of a binary search tree (BST) and a value to insert into the tree. Return the root node of the BST after the insertion. It is guaranteed that the new value does not exist in the original BST.
Notice that there may exist multiple valid ways for the insertion, as long as the tree remains a BST after insertion. You can return any of them.
Example 1
1
2
3
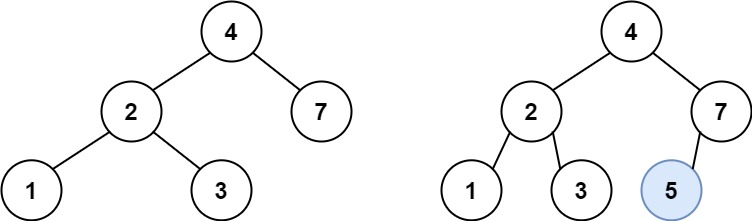
Input: root = [4,2,7,1,3], val = 5
Output: [4,2,7,1,3,5]
Explanation: Another accepted tree is:
Example 2
1
2
Input: root = [40,20,60,10,30,50,70], val = 25
Output: [40,20,60,10,30,50,70,null,null,25]
Example 3
1
2
Input: root = [4,2,7,1,3,null,null,null,null,null,null], val = 5
Output: [4,2,7,1,3,5]
Solution
Python
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
class Solution(object):
def insertIntoBST(self, root, val):
if root is None:
return TreeNode(val)
if val < root.val:
root.left = self.insertIntoBST(root.left, val)
return root
root.right = self.insertIntoBST(root.right, val)
return root
Delete Node in a BST
Given a root node reference of a BST and a key, delete the node with the given key in the BST. Return the root node reference (possibly updated) of the BST.
Basically, the deletion can be divided into two stages:
- Search for a node to remove.
- If the node is found, delete the node.
Example 1
1
2
3
4
5
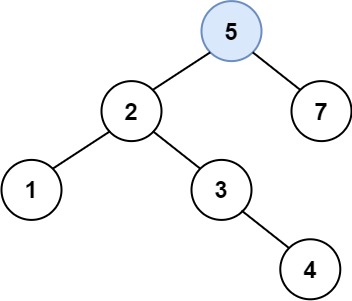
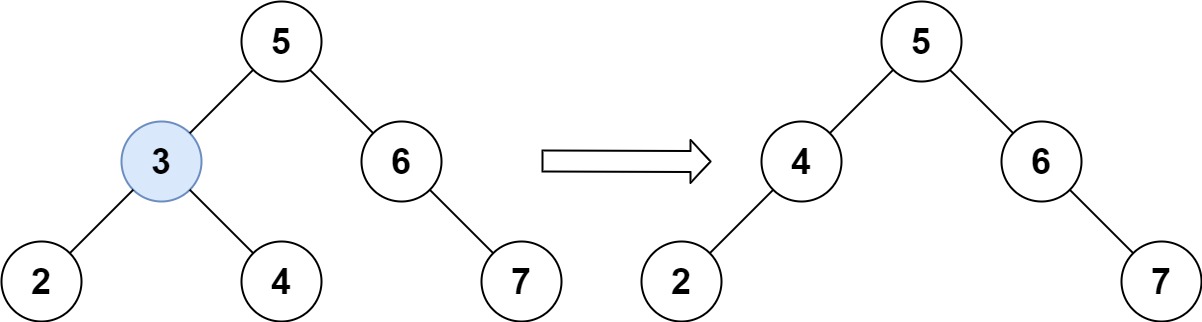
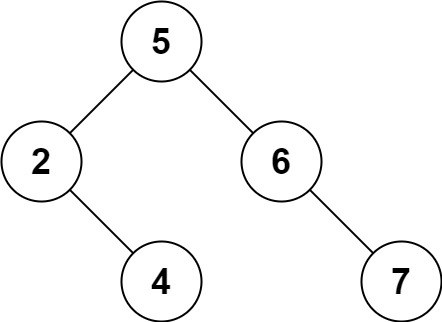
Input: root = [5,3,6,2,4,null,7], key = 3
Output: [5,4,6,2,null,null,7]
Explanation: Given key to delete is 3. So we find the node with value 3 and delete it.
One valid answer is [5,4,6,2,null,null,7], shown in the above BST.
Please notice that another valid answer is [5,2,6,null,4,null,7] and it's also accepted.
Example 2
1
2
3
Input: root = [5,3,6,2,4,null,7], key = 0
Output: [5,3,6,2,4,null,7]
Explanation: The tree does not contain a node with value = 0.
Example 3
1
2
Input: root = [], key = 0
Output: []
Solution
The deletion process involves handling three distinct cases once the node to be deleted is located.
**Case **1: Node is a Leaf (No Child Nodes)
If the node has no left or right child, we simply delete this node by returning None. T
1
2
if not root.left and not root.right:
return None
Case 2: Node has One Child
If the node to be deleted has only one child, we replace the node with its single child. This is done by returning the child node, which will take the place of the deleted node.
- Left Child Only: If the node has only a left child, return the left child.
- Right Child Only: If the node has only a right child, return the right child.
1
2
3
4
if not root.left:
return root.right
elif not root.right:
return root.left
Case 3: Node has Two Children
If the node has two children, this is the most complex case. To maintain the BST properties, we need to:
- Find the smallest node in the right subtree (in-order successor). This node is guaranteed to be larger than all nodes in the left subtree and smaller than all other nodes in the right subtree.
1
min_larger_node = self.findMin(root.right)
- Replace the value of the node to be deleted with the value of the in-order successor. This ensures that the BST property remains intact.
1
root.val = min_larger_node.val
Recursively delete the in-order successor from the right subtree since its value has been moved to the current node. This step ensures that the tree does not contain duplicate values.
1
root.right = self.deleteNode(root.right, min_larger_node.val)
Complete Code
Python
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
class Solution(object):
def deleteNode(self, root, key):
if not root:
return None
if key < root.val:
root.left = self.deleteNode(root.left, key)
elif key > root.val:
root.right = self.deleteNode(root.right, key)
else:
if not root.left:
return root.right
elif not root.right:
return root.left
min_larger_node = self.findMin(root.right)
root.val = min_larger_node.val
root.right = self.deleteNode(root.right, min_larger_node.val)
return root
def findMin(self, node):
while node.left:
node = node.left
return node
Reference
Leetcode-235 Lowest Common Ancestor of a Binary Search Tree: https://leetcode.com/problems/lowest-common-ancestor-of-a-binary-search-tree/description/. ↩︎
代码随想录-二叉搜索树的最近公共祖先: https://programmercarl.com/0235.二叉搜索树的最近公共祖先.html#算法公开课. ↩︎
Leetcode-701 Insert into a Binary Search Tree: https://leetcode.com/problems/insert-into-a-binary-search-tree/description/. ↩︎
代码随想录-二叉搜索树中的插入操作: https://programmercarl.com/0701.二叉搜索树中的插入操作.html. ↩︎
Leetcode-450 Delete Node in a BST: https://leetcode.com/problems/delete-node-in-a-bst/description/. ↩︎
代码随想录-删除二叉搜索树中的节点: https://programmercarl.com/0450.删除二叉搜索树中的节点.html. ↩︎