Leetcode Day 11 - Binary Tree: Traversal Techniques
Focuses on binary tree level order traversal techniques, including regular, N-ary tree, and right-side view traversals. Also calculates averages at each tree level.
Binary Tree
Binary Tree Level Order Traversal
Given the root of a binary tree, return the level order traversal of its nodes’ values. (i.e., from left to right, level by level).
Example 1
1
2
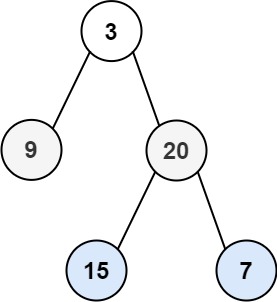
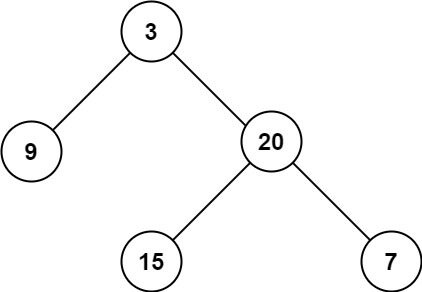
Input: root = [3,9,20,null,null,15,7]
Output: [[3],[9,20],[15,7]]
Example 2
1
2
Input: root = [1]
Output: [[1]]
Example 3
1
2
Input: root = []
Output: []
Solution
Python
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
class Solution(object):
def levelOrder(self, root):
if root is None:
return []
result = []
def traverse(node, level):
if node is None:
return
if len(result) == level:
result.append([])
result[level].append(node.val)
traverse(node.left, level + 1)
traverse(node.right, level + 1)
traverse(root, 0)
return result
Binary Tree Level Order Traversal II
Given the root of a binary tree, return the bottom-up level order traversal of its nodes’ values. (i.e., from left to right, level by level from leaf to root).
Example 1
1
2
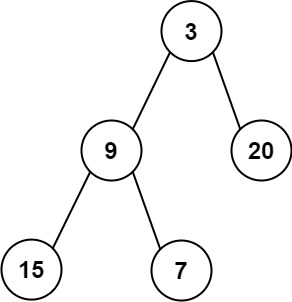
Input: root = [3,9,20,null,null,15,7]
Output: [[15,7],[9,20],[3]]
Example 2
1
2
Input: root = [1]
Output: [[1]]
Example 3
1
2
Input: root = []
Output: []
Solution
Python
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
class Solution(object):
def levelOrderBottom(self, root):
if root is None:
return []
result = []
def traverse(node, level):
if node is None:
return
if len(result) == level:
result.append([])
traverse(node.left, level + 1)
traverse(node.right, level + 1)
result[level].append(node.val)
traverse(root,0)
l = len(result)
for i in range(l // 2):
result[i], result[l - i - 1] = result[l - i - 1], result[i]
return result
Binary Tree Right Side View
Given the root of a binary tree, imagine yourself standing on the right side of it, return the values of the nodes you can see ordered from top to bottom.
Example 1
1
2
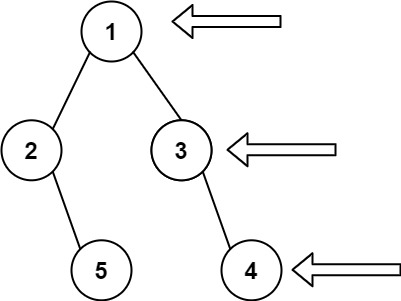
Input: root = [1,2,3,null,5,null,4]
Output: [1,3,4]
Example 2
1
2
Input: root = [1,null,3]
Output: [1,3]
Example 3
1
2
Input: root = []
Output: []
Solution
Python
Iteration Solution
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
class Solution(object):
def rightSideView(self, root):
if root is None:
return []
result = [root.val]
def right_side(node, level):
if node is None:
return
if len(result) <= level:
if node.right is not None:
result.append(node.right.val)
elif node.left is not None:
result.append(node.left.val)
right_side(node.right, level + 1)
right_side(node.left, level + 1)
right_side(root,1)
return result
Loop
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
class Solution(object):
def rightSideView(self, root):
if not root:
return []
queue = collections.deque([root])
right_view = []
while queue:
level_size = len(queue)
for i in range(level_size):
node = queue.popleft()
if i == level_size - 1:
right_view.append(node.val)
if node.left:
queue.append(node.left)
if node.right:
queue.append(node.right)
return right_view
Average of Levels in Binary Tree
Given the root of a binary tree, return the average value of the nodes on each level in the form of an array. Answers within 10<sup>-5</sup> of the actual answer will be accepted.
Example 1
1
2
3
4
Input: root = [3,9,20,null,null,15,7]
Output: [3.00000,14.50000,11.00000]
Explanation: The average value of nodes on level 0 is 3, on level 1 is 14.5, and on level 2 is 11.
Hence return [3, 14.5, 11].
Example 2
1
2
Input: root = [3,9,20,15,7]
Output: [3.00000,14.50000,11.00000]
Solution
Python
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
class Solution(object):
def averageOfLevels(self, root):
sums = [[root.val, 1]]
def average(node, level):
if node is None or (node.left is None and node.right is None):
return
if len(sums) == level:
sums.append([0,0])
if node.left is not None:
sums[level][0] += node.left.val
sums[level][1] += 1
average(node.left, level + 1)
if node.right is not None:
sums[level][0] += node.right.val
sums[level][1] += 1
average(node.right, level + 1)
average(root,1)
for i in range(len(sums)):
sums[i] = float(sums[i][0]) / float(sums[i][1])
return sums
N-ary Tree Level Order Traversal
Given an n-ary tree, return the level order traversal of its nodes’ values.
Nary-Tree input serialization is represented in their level order traversal, each group of children is separated by the null value (See examples).
Example 1
1
2
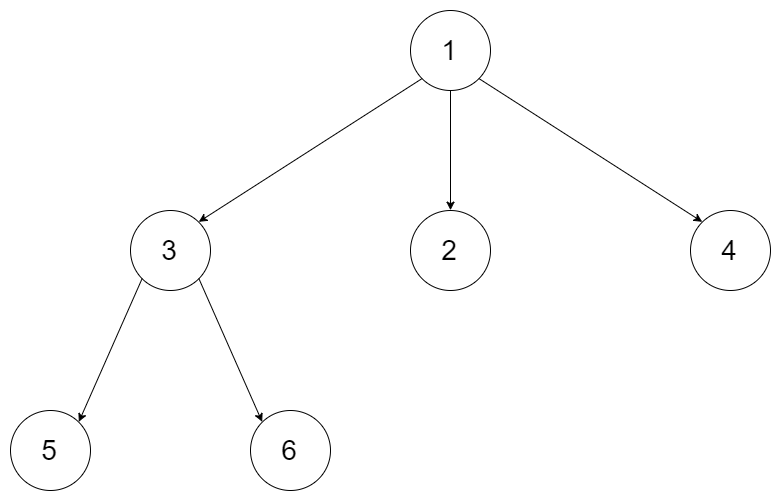
Input: root = [1,null,3,2,4,null,5,6]
Output: [[1],[3,2,4],[5,6]]
Example 2
1
2
Input: root = [1,null,2,3,4,5,null,null,6,7,null,8,null,9,10,null,null,11,null,12,null,13,null,null,14]
Output: [[1],[2,3,4,5],[6,7,8,9,10],[11,12,13],[14]]
Solution
Python
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
class Solution(object):
def levelOrder(self, root):
result =[]
def level_order(node, level):
if node is None:
return
if len(result) == level:
result.append([])
result[level].append(node.val)
for child in node.children:
level_order(child, level + 1)
level_order(root, 0)
return result
Find Largest Value in Each Tree Row
Example 1
1
2
Input: root = [1,3,2,5,3,null,9]
Output: [1,3,9]
Example 2
1
2
Input: root = [1,2,3]
Output: [1,3]
Solution
Python
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
class Solution(object):
def largestValues(self, root):
result = []
def largest(node, level):
if node is None:
return
if len(result) == level:
result.append(node.val)
else:
result[level] = max(result[level], node.val)
largest(node.left, level + 1)
largest(node.right, level + 1)
largest(root, 0)
return result
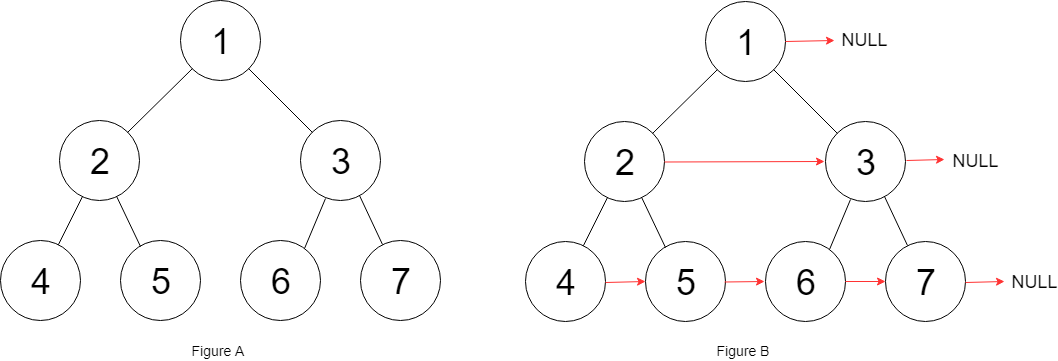
Populating Next Right Pointers in Each Node
You are given a perfect binary tree where all leaves are on the same level, and every parent has two children. The binary tree has the following definition:
1
2
3
4
5
6
struct Node {
int val;
Node *left;
Node *right;
Node *next;
}
Populate each next pointer to point to its next right node. If there is no next right node, the next pointer should be set to NULL.
Initially, all next pointers are set to NULL.
Example 1
1
2
3
Input: root = [1,2,3,4,5,6,7]
Output: [1,#,2,3,#,4,5,6,7,#]
Explanation: Given the above perfect binary tree (Figure A), your function should populate each next pointer to point to its next right node, just like in Figure B. The serialized output is in level order as connected by the next pointers, with '#' signifying the end of each level.
Example 2
1
2
Input: root = []
Output: []
Solution
Python
Iteration
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
class Solution(object):
def connect(self, root):
if root is None:
return None
def populate(node, nex):
if node.left is None:
return
node.left.next = node.right
node.right.next = nex
populate(node.left, node.right.left)
if nex is not None:
populate(node.right, nex.left)
else:
populate(node.right, None)
populate(root, None)
return root
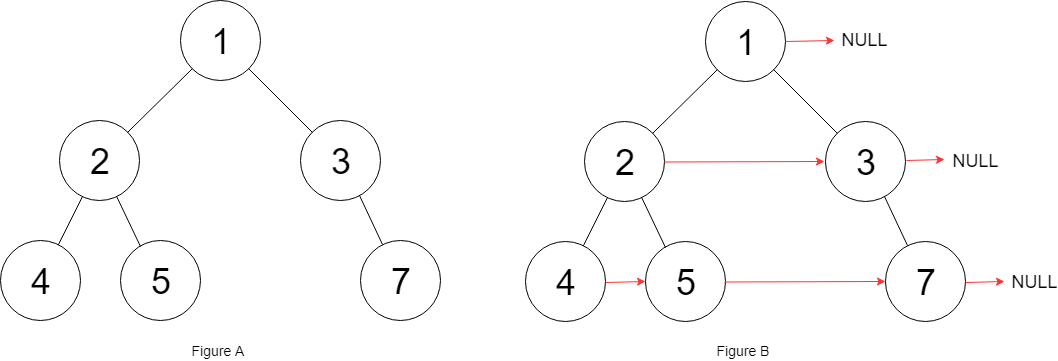
Populating Next Right Pointers in Each Node II
Given a binary tree
1
2
3
4
5
6
struct Node {
int val;
Node *left;
Node *right;
Node *next;
}
Populate each next pointer to point to its next right node. If there is no next right node, the next pointer should be set to NULL.
Initially, all next pointers are set to NULL.
Example 1
1
2
3
Input: root = [1,2,3,4,5,null,7]
Output: [1,#,2,3,#,4,5,7,#]
Explanation: Given the above binary tree (Figure A), your function should populate each next pointer to point to its next right node, just like in Figure B. The serialized output is in level order as connected by the next pointers, with '#' signifying the end of each level.
Example 2
1
2
Input: root = []
Output: []
Solution
Python
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
class Solution(object):
def connect(self, root):
next_points = []
def populate(node, level):
if node is None:
return
if len(next_points) == level:
next_points.append(node)
else:
node.next = next_points[level]
next_points[level] = node
populate(node.right, level + 1)
populate(node.left, level + 1)
populate(root, 0)
return root
Maximum Depth of Binary Tree
Example 1
1
2
Input: root = [3,9,20,null,null,15,7]
Output: 3
Example 2
1
2
Input: root = [1,null,2]
Output: 2
Solution
Python
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
class Solution(object):
def maxDepth(self, root):
def depth_of(node, depth):
if node is None:
return depth
return 1 + max(depth_of(node.left, depth), depth_of(node.right, depth))
return depth_of(root, 0)
Minimum Depth of Binary Tree
Given a binary tree, find its minimum depth.
The minimum depth is the number of nodes along the shortest path from the root node down to the nearest leaf node.
Note: A leaf is a node with no children.
Example 1
1
2
Input: root = [3,9,20,null,null,15,7]
Output: 2
Example 2
1
2
Input: root = [2,null,3,null,4,null,5,null,6]
Output: 5
Solution
Python
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
class Solution(object):
def minDepth(self, root):
if root is None:
return 0
depth = 1
if root.left is not None and root.right is not None:
depth += min(self.minDepth(root.left), self.minDepth(root.right))
elif root.left is not None:
depth += self.minDepth(root.left)
elif root.right is not None:
depth += self.minDepth(root.right)
return depth
Reference
Leetcode-102 Binary Tree Level Order Traversal: https://leetcode.com/problems/binary-tree-level-order-traversal/description/. ↩︎
代码随想录-二叉树的层序遍历 II: https://programmercarl.com/0102.二叉树的层序遍历.html. ↩︎ ↩︎2 ↩︎3 ↩︎4 ↩︎5 ↩︎6 ↩︎7 ↩︎8 ↩︎9 ↩︎10
Leetcode-107 Binary Tree Level Order Traversal II: https://leetcode.com/problems/binary-tree-level-order-traversal-ii/description/. ↩︎
Leetcode-199 Binary Tree Right Side View: https://leetcode.com/problems/binary-tree-right-side-view/description/. ↩︎
Leetcode-637 Average of Levels in Binary Tree: https://leetcode.com/problems/average-of-levels-in-binary-tree/description/. ↩︎
Leetcode-429 N-ary Tree Level Order Traversal: https://leetcode.com/problems/n-ary-tree-level-order-traversal/description/. ↩︎
Leetcode-515 Find Largest Value in Each Tree Row: https://leetcode.com/problems/find-largest-value-in-each-tree-row/description/. ↩︎
Leetcode-116 Populating Next Right Pointers in Each Node: https://leetcode.com/problems/populating-next-right-pointers-in-each-node/description/. ↩︎
Leetcode-117 Populating Next Right Pointers in Each Node II: https://leetcode.com/problems/populating-next-right-pointers-in-each-node-ii/description/. ↩︎
Leetcode-104 Maximum Depth of Binary Tree: https://leetcode.com/problems/maximum-depth-of-binary-tree/description/. ↩︎
Leetcode-111 Minimum Depth of Binary Tree: https://leetcode.com/problems/minimum-depth-of-binary-tree/description/. ↩︎