Hash Table
Hash table | Technique to handle collisions | Hash table in Python and Java
Related Leetcode Questions
Hash Table
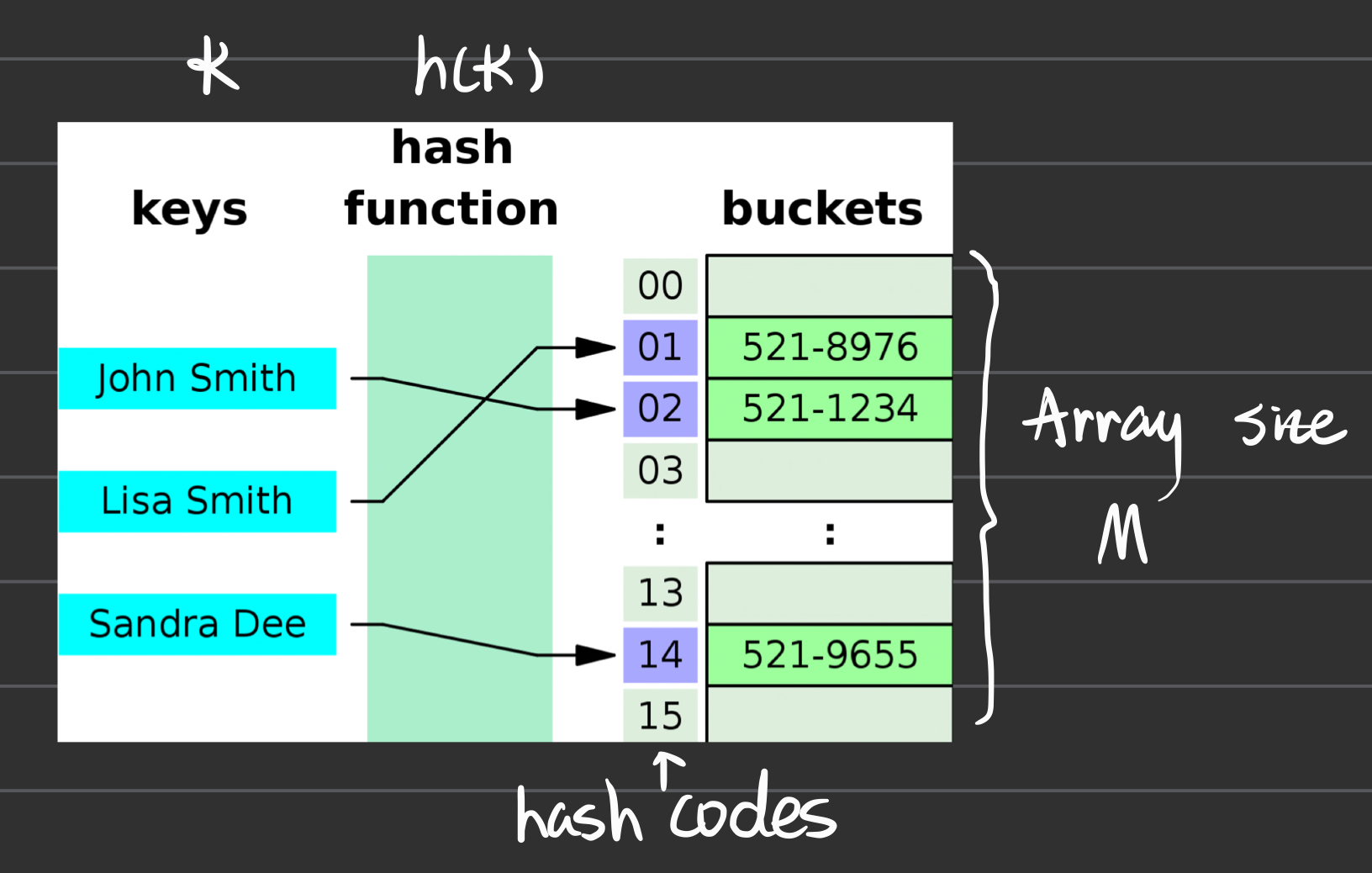
A structure that can map keys to values. It uses a hash function to compute an index into an array of buckets or slots, from which the desired value can be found in time O(1).
Collisions
There can be different keys (k_1), (k_2) for which (h(k_1) = h(k_2))
\[h(k_1) = h(k_2)\]Technique to handle collisions
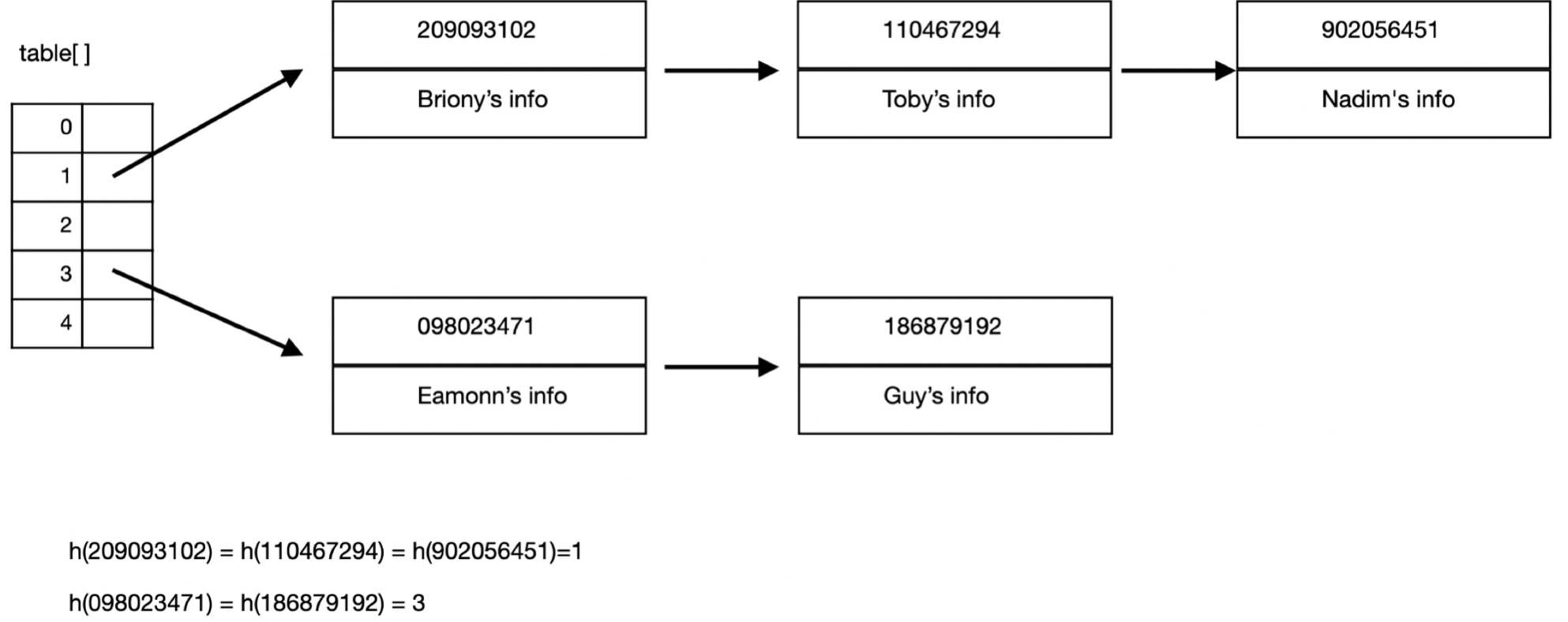
Chaining
Each bucket in the hash table points to a linked list of entries that hash to the same index. When a collision occurs, the new entry is added to the list.
Open addressing
Instead of storing all entries that hash to the same index in a linked list, open addressing searches for the next available slot in the array, make use of spare space, for example:
- Linear probing: Scan forward through the array. If the desired slot is occupied, check the next slot, and so on.
- Quadratic probing: Reduces primary clustering by checking slots at increasing distances.
- (h(k,i) = (h(k) + c_1 i + c_2 i^2) \% M)
- Double hashing: Uses a secondary hash function to determine the interval between probes, providing a more uniform distribution of entries.
- (H(k,i) = (h_1(k) + i \cdot h_2(k)) \% M)
Hash Table in Python
ord()
The ord() function in Python returns an integer representing the ASCII / Unicode code point of the given character.
Example
1
2
3
4
5
6
>>>ord('a')
97
>>> ord('b')
98
>>> ord('c')
99
Dictionary dict
Python’s built-in hash table. It uses an array where each slot is a linked list of key-value pairs (to handle collisions).
Example
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
# Creating a dictionary
my_dict = {'key1': 'value1', 'key2': 'value2'}
# Accessing values
value = my_dict['key1']
# Adding a new key-value pair
my_dict['key3'] = 'value3'
# Removing a key-value pair
del my_dict['key2']
Set
A collection which is unordered, unchangeable*, and unindexed. No duplicate members.
Exxample
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
# Creating a set
my_set = {'a', 'b', 'c'}
# Adding an element
my_set.add('d')
# Removing an element
my_set.remove('b')
# Checking membership
if 'a' in my_set:
print("Found 'a' in set")
Advanced Specialized Libraries
collections.defaultdict: A dictionary subclass that calls a factory function to supply missing values.collections.OrderedDict: A dictionary subclass that remembers the order entries were added.collections.Counter: A dictionary subclass for counting hashable objects.
Hash Table in Java
HashMap
The most commonly used class for implementing hash tables in Java. It allows null keys and values and provides constant-time performance for basic operations (get and put).
Example
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
import java.util.HashMap;
HashMap<String, String> myMap = new HashMap<>();
// Adding key-value pairs
myMap.put("key1", "value1");
myMap.put("key2", "value2");
// Accessing values
String value = myMap.get("key1");
// Removing a key-value pair
myMap.remove("key2");
HashSet
Implements the Set interface and uses a hash table for storage, ensuring that no duplicate elements are stored.
Example
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
import java.util.HashSet;
HashSet<String> mySet = new HashSet<>();
// Adding elements
mySet.add("a");
mySet.add("b");
// Removing an element
mySet.remove("b");
// Checking membership
if (mySet.contains("a")) {
System.out.println("Found 'a' in set");
}
Other Related Classes
Hashtable: Similar to HashMap but does not allow null keys or values. Hashtable is synchronized, making it thread-safe.LinkedHashMap: Extends HashMap and maintains a linked list of the entries in the map, in the order in which they were inserted.TreeMap: A Map implementation that keeps its entries sorted according to the natural ordering of its keys or by a specified comparator.